Knee pain is a common complaint for which there can be many causes. It is important to make an accurate diagnosis of the cause of your symptoms so that appropriate treatment can be directed at the cause. Your knee joint is made up of bone, cartilage, ligaments and fluid. Muscles and tendons help the knee joint move properly. When any of these structures is injured or diseased, then knee problems will result causing pain and difficulty walking.
Joint Solutions Orthopaedics specializes in the treatment of many orthopedic conditions including treatments for many knee pain conditions and injuries.
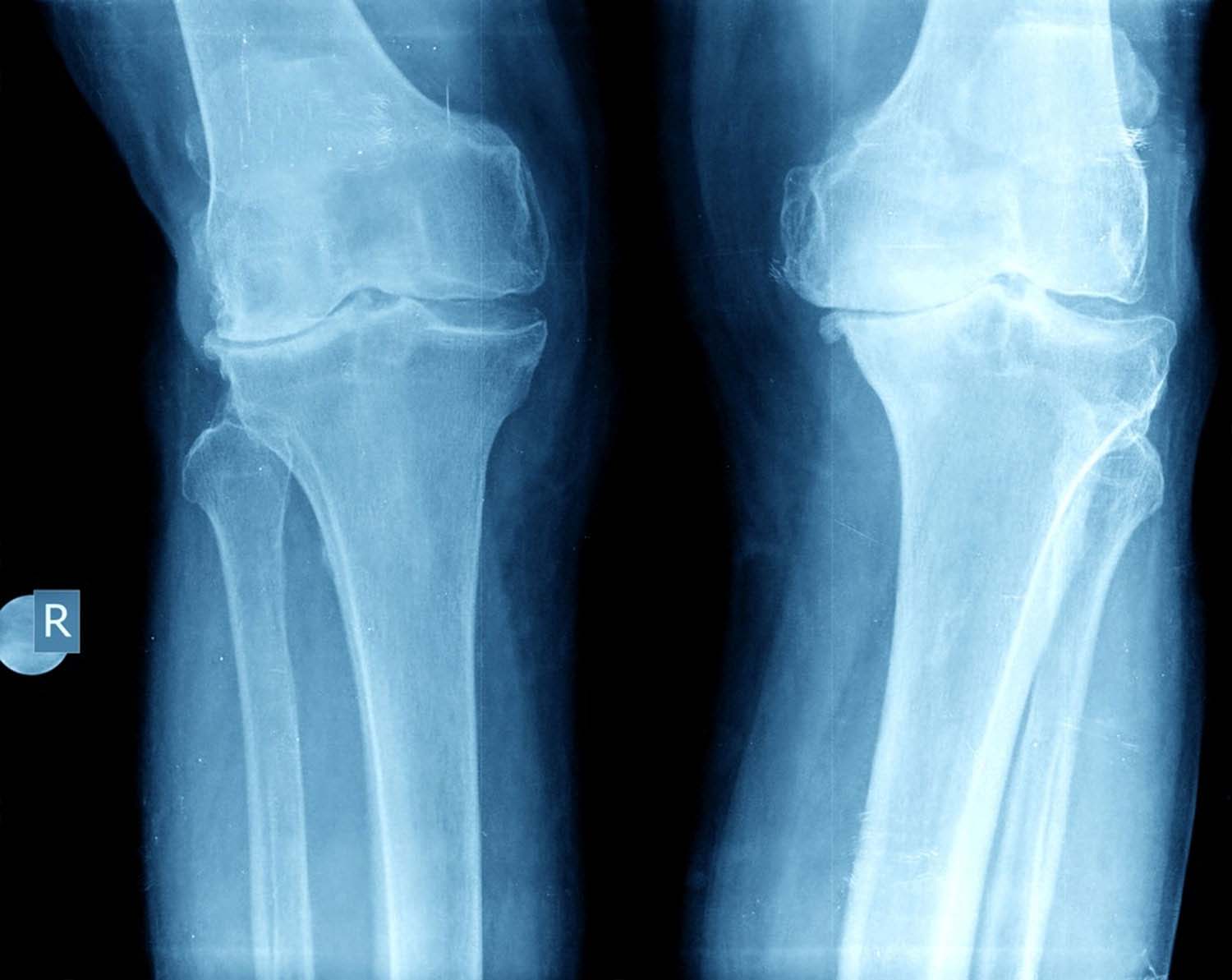
Occurs when there is wearing away or destruction of the cartilage either as a degenerative process or an inflammatory or traumatic process. Types: Osteoarthritis (OA) or Inflammatory arthritis (eg Rheumatoid arthritis RA) or post traumatic arthritis.
In OA of the knee the cartilage wears away leading to the rough bone ends which tend to rub against each other leading to pain and stiffness. In RA the immune system attacks its own normal tissues (cartilage and ligaments) causing damage. The synovial membrane gets inflamed leading to pain and stiffness.
Post traumatic arthritis occurs when there is cartilage injury after a fracture or due to cartilage damage. It can also occurs after ligament and meniscus injury which lead to instability and further wear of the joint.
The 4 major ligaments supporting the knee are :
The usual mode of injury to these ligaments is traumatic in nature. Depending on the activity at the time of injury, position of the leg and knee and direction of force, one or more than one ligament may be injured or torn with or without injury to other knee structures.
Cause: Changing direction abruptly, rapidly; Incorrect landing mechanics after a jump, direct contact injury.
They lie to the side of the knee and control the sideways motion
Cause: Usually by a force that pushes the knee sideways.
Uncommon compared to other ligaments.
Cause: Direct blow to front of the knee or hyperextension injury.
Mild Sprain (Grade 1) to Complete Tear (Grade 3)
Meniscus is a C shaped disc which acts a shock absorber between the leg bone and thigh bone. It helps stabilize the knee and provide for smooth kinematics. It can get injured due to sudden acute twisting or can be degenerative in nature due to gradual wearing out.
Depends on nature, type and location of tear
Pain specifically located in the kneecap can cause acute symptoms at the time of injury but can also lead to chronic knee pain.
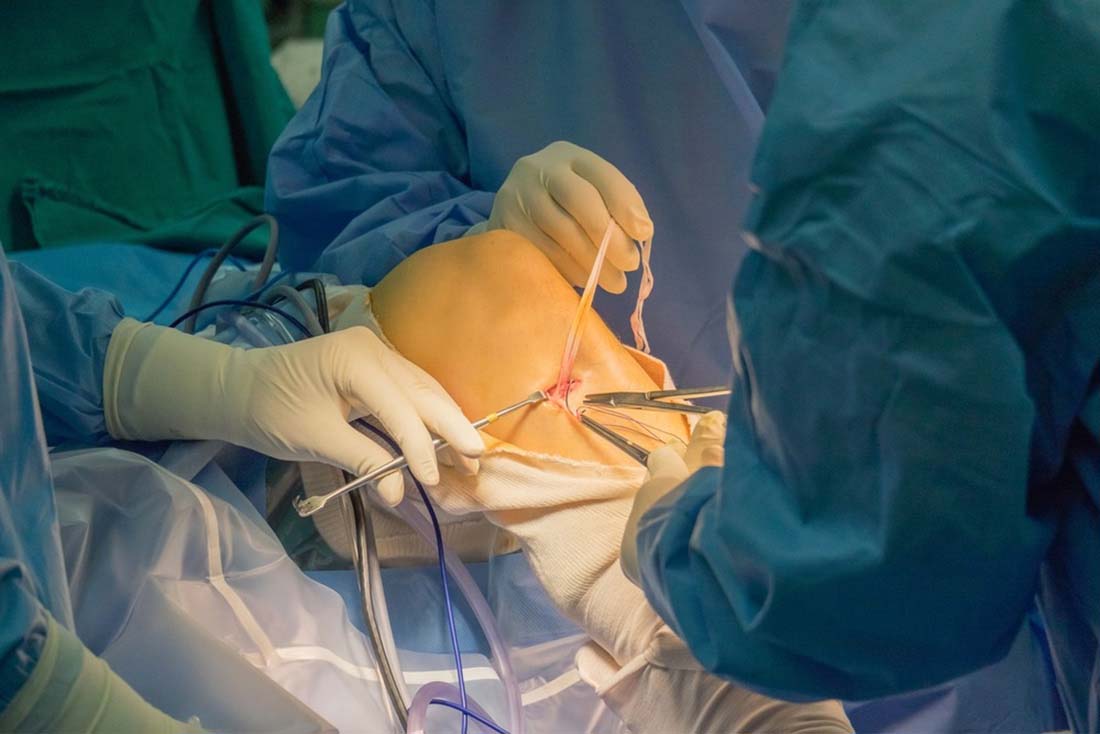
Patellar dislocation can be due to trauma (direct injury or fall) or due to muscle imbalance. Either situation can lead to recurrent instability. Pain is the predominant symptom followed by bucking, instability and knee swelling.
Non Surgical treatment: Immobilization ,protected weight bearing and physical therapy.
Surgical Treatment: in cases of recurrent disclocation or failure to respond to non surgical treatment surgery is needed. This incudes MPFL reconstruction, bony osteotomy and realignment procedures.
Patellofemoral arthritis: Pain in front of the knee. Difficulty in squatting, kneeling and staircase climbing. The cartilage on the undersurface of thse patella and overlying the trochlea wears away. This can occur due to malalignment of the patella, trauma or due to dysplasia of the trochlea. Non Surgical treatment includes activity modifications, rest, medications, physical therapy, bracing, injections
Surgical treatment:These injuries are seen in both young and older populations and can be a common cause of knee pain.
Can be traumatic in nature or secondary to degenerative process The cartilage cover at the ends of the bone may be injured leading to loose body formation or an unstable chondral flap. In these conditions fixing the cartilage defect, debriding the chondral flap or arthroscopy excision of the loose body need to be done. In some cases cartilage reconstructive procedure may be necessary. Non-Surgical treatment can be done for degenerative cartilage problems by modifying activity and physical therapy.
Young adults can suffer from genetic malformations that cause knee pain but are also at an increased risk for knee trauma due to athletic injuries.